What is a government?
A government is an organized system or institution through which a society or community is governed. It establishes and enforces laws, policies, and rules to maintain order, provide services, and protect the rights and safety of its people. Governments can take various forms, but they typically include structures of authority and decision-making, such as legislatures, executives, and judicial systems.

https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/United_States
Functions of a Government:
- Maintaining Order: Establishing and enforcing laws to prevent chaos and ensure public safety.
- Providing Services: Offering public goods and services, such as education, healthcare, infrastructure, and public transportation.
- Protecting Rights: Safeguarding the fundamental rights and freedoms of individuals.
- Defense and Security: Protecting the nation from external threats and maintaining internal security.
- Economic Management: Regulating the economy, managing public funds, and promoting economic stability and growth.
- Diplomacy: Managing relations with other countries and international organizations.
Types of Government:
- Democracy: Power is held by the people, often through elected representatives (e.g., the United States, India).
- Monarchy: Power is vested in a king or queen, which can be constitutional (e.g., the UK) or absolute (e.g., Saudi Arabia).
- Authoritarianism: Power is concentrated in a single leader or small group, with limited political freedoms (e.g., North Korea).
- Communism: A system where the government owns and controls resources and production (e.g., China, Cuba).
- Republic: A government in which the people elect representatives and a leader, often a president, to make decisions on their behalf (e.g., France).
- Federal System: Power is shared between a central government and regional governments (e.g., the United States, Germany).
Each government is shaped by its constitution, history, culture, and social norms, influencing how it operates and interacts with its citizens.
Examples:
Democracy
- Example: The United States
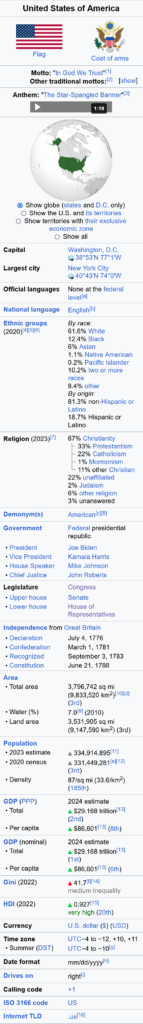
- The U.S. is a federal democratic republic where power is shared between the national and state governments. Leaders are elected by citizens, and laws are passed by representatives in Congress. The president serves as the head of state and government.
- Example: India
- India is the world’s largest democracy. Citizens vote in regular elections to choose representatives for the parliament, and the prime minister leads the government.
Monarchy
- Constitutional Monarchy:
- Example: United Kingdom
- The king or queen is the ceremonial head of state, while elected officials like the prime minister and Parliament handle governance.
- Example: United Kingdom
- Absolute Monarchy:
- Example: Saudi Arabia
- The king has significant control over laws and governance, and there is no elected parliament to limit the monarch’s power.
- Example: Saudi Arabia
Authoritarianism
- Example: North Korea
- Power is concentrated in the hands of the leader, Kim Jong Un, with strict control over all aspects of life, including the economy, media, and individual freedoms.
- Example: Syria
- Under President Bashar al-Assad, the government exercises extensive control over political and civil liberties, often through military and police force.
Communism
- Example: China
- The Communist Party controls the government and economy. While there is some economic liberalization, political power remains centralized under party leadership.
- Example: Cuba
- The government owns most industries and resources, with policies guided by the Communist Party.
Republic
- Example: France
- France operates as a unitary semi-presidential republic. Citizens elect representatives to the National Assembly and a president who shares power with a prime minister.
- Example: South Africa
- A parliamentary republic where the president is elected by the National Assembly, and laws are passed by elected representatives.
Federal System
- Example: United States
- States have their own governments and laws, but they are united under a federal system governed by the Constitution.
- Example: Germany
- A federal parliamentary republic where power is shared between the federal government and the Länder (states).
Other Forms of Government
- Theocracy:
- Example: Iran
- A government where religious leaders hold significant power. Iran’s Supreme Leader, a cleric, oversees the state based on Islamic principles.
- Example: Iran
- Socialist State:
- Example: Venezuela
- The government plays a significant role in the economy, aiming to reduce inequality by controlling key industries and redistributing resources.
- Example: Venezuela
These examples highlight the diversity of government structures worldwide and their influence on citizens’ lives.
A government is a group of people who are in charge of running a country, state, or community. Think of it like the leaders of your school — the principal, teachers, and school board. They make rules, solve problems, and keep things running smoothly so everyone can learn and stay safe. Governments do this for entire countries or regions.
Examples of Different Types of Governments:
- Democracy (Power to the People):
- In a democracy, people vote to choose their leaders, like voting for a class president.
- Example: In the United States, citizens vote for the president, governors, and lawmakers.
- Monarchy (King or Queen in Charge):
- A monarchy is like having a king or queen in charge. Some monarchs have lots of power, while others are more like symbols.
- Example: In the United Kingdom, there’s a king, but the real decisions are made by elected leaders.
- Example: In Saudi Arabia, the king makes most of the big decisions.
- Authoritarianism (One Leader Has All the Power):
- In this type of government, one person or a small group decides everything, and people don’t get to vote or speak out much.
- Example: In North Korea, the leader, Kim Jong Un, makes all the rules, and people must follow them.
- Communism (Sharing Everything):
- In a communist government, the leaders control most of the resources, like land and businesses, and they try to make sure everyone gets the same.
- Example: In China, the government owns most businesses and decides how things are shared.
- Republic (Elected Representatives):
- In a republic, people vote for leaders to make decisions for them, like electing a city council to decide things for a town.
- Example: In France, people vote for a president and lawmakers to represent them.
- Theocracy (Religion Rules):
- In a theocracy, the government is run based on religious beliefs.
- Example: In Iran, the leaders use Islamic laws to guide their decisions.
What Do Governments Do?
- Make Rules: Like your school’s rules, governments create laws to keep people safe and help things run smoothly.
- Protect People: Governments have police and armies to keep people safe from danger.
- Provide Services: They do things like build roads, run schools, and provide healthcare.
- Help Solve Problems: If there’s a big issue, like a storm or a fire, the government helps people recover.
Governments are like the leaders of a big group, and they help make sure things work for everyone!